Air Pollution

Air pollution, a complex and pervasive environmental issue, poses a significant threat to human health and the planet’s ecosystems. It arises from the release of various harmful substances into the atmosphere, leading to a decline in air quality. Understanding the sources, types, effects, and solutions to air pollution is crucial for mitigating its devastating consequences.
Sources of Air Pollution:
- Industrial Emissions:
- Factories and power plants release pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Manufacturing processes involving chemicals, metals, and fossil fuel combustion contribute significantly to air pollution.
- Transportation:
- Vehicular emissions, including cars, trucks, and airplanes, are a major source of pollutants like NOx, PM, carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons.
- The increasing number of vehicles and reliance on fossil fuels exacerbate this problem.
- Residential and Commercial Activities:
- Burning wood, coal, and other fuels for heating and cooking releases pollutants into the air.
- Construction activities, dust from roads, and the use of certain consumer products also contribute to air pollution.
- Agricultural Activities:
- Livestock farming releases methane (CH₄), a potent greenhouse gas.
- The use of fertilizers and pesticides can lead to the release of ammonia (NH₃) and other harmful substances.
- Burning of crop residue.
- Natural Sources:
- Volcanic eruptions release ash, gases, and particulate matter into the atmosphere.
- Wildfires produce smoke and particulate matter.
- Wind erosion can create dust storms.
Types of Air Pollutants:
- Particulate Matter (PM):
- Tiny particles suspended in the air, including dust, soot, and smoke.
- PM10 (particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less) and PM2.5 (particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less) are particularly harmful to human health.
- Gaseous Pollutants:
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Formed from the combustion of fossil fuels, contributing to smog and acid rain.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): Released from burning fossil fuels, especially coal, and contributing to acid rain and respiratory problems.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion, which can be fatal in high concentrations.
- Ozone (O₃): Ground-level ozone, formed from the reaction of NOx and VOCs in the presence of sunlight, is a major component of smog.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Released from various sources, including solvents, paints, and industrial processes, contributing to ozone formation.
- Ammonia (NH₃): From agricultural processes.
- Greenhouse Gases:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A major contributor to climate change, released from the burning of fossil fuels.
- Methane (CH₄): A potent greenhouse gas released from agriculture, waste decomposition, and fossil fuel production.
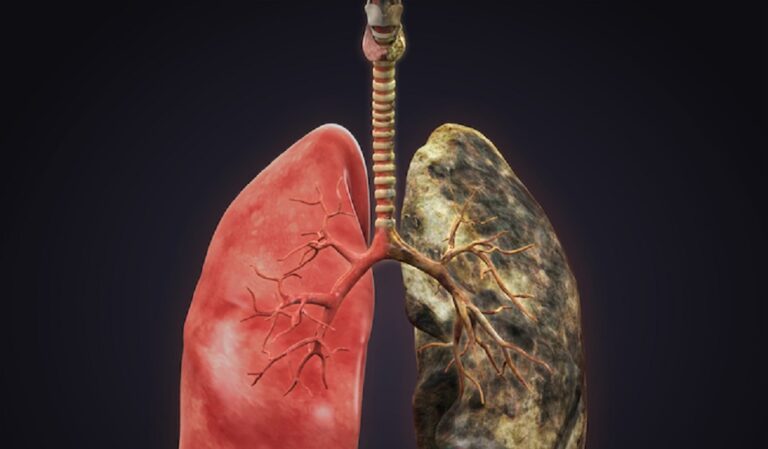
Effects of Air Pollution:
- Human Health:
- Respiratory problems, such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
- Cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Increased risk of infections and allergies.
- Neurological effects, especially in children.
- Premature death.
- Environmental Impacts:
- Acid rain, which damages forests, lakes, and buildings.
- Ozone depletion, which increases exposure to harmful UV radiation.
- Climate change, caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases.
- Damage to ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Reduced crop yields.
- Smog.
- Economic Impacts:
- Increased healthcare costs.
- Reduced productivity.
- Damage to infrastructure.
- Losses in agriculture and tourism.
Solutions to Air Pollution:
- Transition to Renewable Energy:
- Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Improved Transportation:
- Promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking.
- Encouraging the use of electric vehicles.
- Implementing stricter emission standards for vehicles.
- Industrial Regulations:
- Enforcing stricter emission standards for industries.
- Investing in cleaner technologies.
- Carbon capture and storage.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- Reducing livestock emissions.
- Using sustainable farming practices.
- Reducing the use of fertilizers.
- Urban Planning:
- Creating green spaces and promoting sustainable urban development.
- Improving public transit systems.
- International Cooperation:
- Implementing international agreements to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sharing technologies and best practices.
- Individual Actions:
- Reducing energy consumption.
- Using public transportation or cycling.
- Recycling and reducing waste.
- Supporting sustainable products.
Addressing air pollution requires a concerted effort from governments, industries, and individuals. By implementing sustainable practices and investing in cleaner technologies, we can improve air quality and protect the health of our planet and its inhabitants.
Other Posts