Oral health
Oral health is a critical component of overall well-being, influencing not only our ability to eat and speak but also impacting systemic health. Neglecting oral hygiene can lead to a range of problems, from cavities and gum disease to more severe conditions. This article delves into the importance of oral health, common issues, and effective preventive measures.
The Importance of Oral Health:
- Functionality:
- Healthy teeth and gums are essential for chewing, swallowing, and proper digestion.
- They play a vital role in clear speech and communication.
- Healthy teeth and gums are essential for chewing, swallowing, and proper digestion.
- Aesthetics:
- A healthy smile contributes to self-confidence and social interactions.
- A healthy smile contributes to self-confidence and social interactions.
- Systemic Health:
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Diabetes complications.
- Respiratory infections.
- Pregnancy complications. Oral bacteria can enter the bloodstream and contribute to systemic diseases, including:
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Pain Prevention:
- Untreated oral problems can cause severe pain, impacting quality of life.
- Untreated oral problems can cause severe pain, impacting quality of life.
Common Oral Health Issues:
- Dental Caries (Cavities):
- Caused by bacteria that produce acids, eroding tooth enamel.
- Leads to tooth decay and potential tooth loss.
- Caused by bacteria that produce acids, eroding tooth enamel.
- Gingivitis:
- Inflammation of the gums, often caused by plaque buildup.
- Symptoms include red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
- Can progress to periodontitis if left untreated.
- Inflammation of the gums, often caused by plaque buildup.
- Periodontitis:
- A severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth.
- Can lead to tooth loss and systemic health problems.
- A severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth.
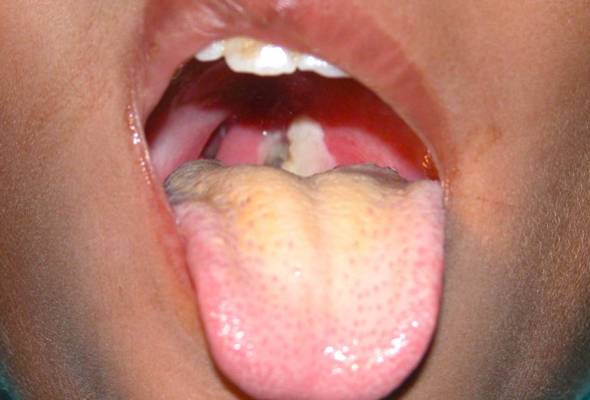
- Oral Thrush (Candidiasis):
- A fungal infection that causes white lesions in the mouth.
- Common in infants, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those using certain medications.
- A fungal infection that causes white lesions in the mouth.
- Oral Cancer:
- Cancer that develops in the mouth, throat, or lips.
- Risk factors include tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and HPV infection.
- Cancer that develops in the mouth, throat, or lips.
- Halitosis (Bad Breath):
- Often caused by poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, or underlying medical conditions.
- Often caused by poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, or underlying medical conditions.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
- Affect the joint that connects the jaw to the skull, causing pain and dysfunction.
Effective Preventive Measures:
- Brushing:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions.
- Brush for at least two minutes, ensuring all surfaces of the teeth are cleaned.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing:
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and below the gumline.
- This helps prevent cavities and gum disease.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and below the gumline.
- Mouthwash:
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Choose a mouthwash that is ADA-accepted.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Regular Dental Checkups:
- Visit your dentist for professional cleanings and examinations at least twice a year.
- Early detection and treatment of oral problems can prevent serious complications.
- Healthy Diet:
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, which contribute to tooth decay.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Increase water consumption.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, which contribute to tooth decay.
- Avoid Tobacco and Excessive Alcohol:
- Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of oral cancer and gum disease.
- Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of oral cancer and gum disease.
- Protect Your Teeth:
- Wear a mouthguard during sports to prevent dental injuries.
- Avoid using your teeth to open packages or other objects.
- Wear a mouthguard during sports to prevent dental injuries.
- Manage Dry Mouth:
- If you experience dry mouth, drink plenty of water, chew sugar-free gum, or use saliva substitutes.
- If you experience dry mouth, drink plenty of water, chew sugar-free gum, or use saliva substitutes.
- Early Intervention for Children:
- Establish good oral hygiene habits early in childhood.
- Regular dental checkups are important for children.
- Establish good oral hygiene habits early in childhood.
Special Considerations:
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes can increase the risk of gum disease.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to gum infections.
- Older Adults: Age-related changes can increase the risk of dry mouth, gum disease, and tooth loss.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems: Are at higher risk for oral infections.
Maintaining good oral health is an investment in your overall well-being. By adopting healthy habits and seeking regular dental care, you can prevent oral problems and enjoy a healthy smile for life.
I hope this information is helpful.
Other Posts