Sexual health

Sexual health is a state of physical, emotional, mental, and social well-being in relation to sexuality. It’s not merely the absence of disease, dysfunction, or infirmity. It requires a positive and respectful approach to sexuality and sexual relationships, as well as the possibility of having pleasurable and safe sexual experiences, free of coercion, discrimination, and violence.
Key Components of Sexual Health:
- Physical Health:
- This includes the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), access to contraception, and management of sexual dysfunction.
- It also includes understanding and managing one’s own body, including reproductive health.
- This includes the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), access to contraception, and management of sexual dysfunction.
- Emotional Health:
- This involves developing healthy sexual relationships based on respect, consent, and open communication.
- It also encompasses managing feelings related to sexuality, such as body image, sexual identity, and sexual orientation.
- This involves developing healthy sexual relationships based on respect, consent, and open communication.
- Mental Health:
- This involves addressing any psychological or emotional issues that may affect sexual function or satisfaction.
- It also includes dealing with the impact of sexual trauma or abuse.
- This involves addressing any psychological or emotional issues that may affect sexual function or satisfaction.
- Social Health:
- This involves understanding the social and cultural factors that influence sexuality, such as gender roles, societal norms, and cultural beliefs.
- It also includes advocating for sexual and reproductive rights.
- This involves understanding the social and cultural factors that influence sexuality, such as gender roles, societal norms, and cultural beliefs.
Essential Aspects of Sexual Health:
- Sexual Rights:
- These are fundamental human rights related to sexuality, including the right to sexual autonomy, sexual expression, and sexual pleasure.
- They also include the right to be free from sexual violence, discrimination, and coercion.
- These are fundamental human rights related to sexuality, including the right to sexual autonomy, sexual expression, and sexual pleasure.
- Sexual Education:
- Comprehensive sexual education provides accurate and age-appropriate information about sexuality, including:
- Reproductive health.
- STIs.
- Contraception.
- Consent.
- Healthy relationships.Sexual orientation and gender identity.
- Comprehensive sexual education provides accurate and age-appropriate information about sexuality, including:
- Sexual and Reproductive Health Services:
- Access to quality sexual and reproductive health services is essential, including:
- STI testing and treatment.
- Contraception counseling and provision.
- Prenatal care.
- Safe abortion services (where legally permitted).
- Management of sexual dysfunction.
- Counseling for sexual assault survivors.
- STI testing and treatment.
- Access to quality sexual and reproductive health services is essential, including:
- Consent:
- Consent is a crucial aspect of healthy sexual relationships.
- It must be freely given, informed, and ongoing.
- Consent can be withdrawn at any time.
- Consent is a crucial aspect of healthy sexual relationships.
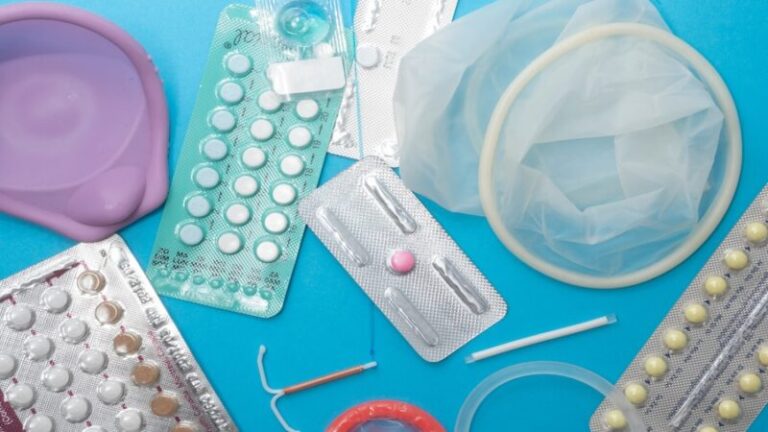
- Safe Sex Practices:
- Practicing safe sex is essential for preventing STIs and unintended pregnancies.
- This includes using condoms consistently and correctly, getting tested regularly, and communicating openly with partners.
- Practicing safe sex is essential for preventing STIs and unintended pregnancies.
- Communication:
- Open and honest communication with partners is crucial for healthy sexual relationships.
- This includes discussing sexual desires, boundaries, and concerns.
- Open and honest communication with partners is crucial for healthy sexual relationships.
Factors Affecting Sexual Health:
- Social and Cultural Norms:
- Societal attitudes and beliefs about sexuality can significantly impact sexual health.
- Societal attitudes and beliefs about sexuality can significantly impact sexual health.
- Gender Inequality:
- Gender inequality can lead to sexual violence, discrimination, and limited access to sexual and reproductive health services.
- Gender inequality can lead to sexual violence, discrimination, and limited access to sexual and reproductive health services.
- Poverty:
- Poverty can restrict access to healthcare, education, and other resources that are essential for sexual health.
- Poverty can restrict access to healthcare, education, and other resources that are essential for sexual health.
- Discrimination:
- Discrimination based on sexual orientation, gender identity, or other factors can negatively affect sexual health.
- Discrimination based on sexual orientation, gender identity, or other factors can negatively affect sexual health.
- Lack of Education:
- Lack of access to accurate sexual education can lead to risky sexual behaviors and poor sexual health outcomes.
- Lack of access to accurate sexual education can lead to risky sexual behaviors and poor sexual health outcomes.
Promoting Sexual Health:
- Comprehensive Sexual Education:
- Providing accurate and age-appropriate sexual education to young people.
- Providing accurate and age-appropriate sexual education to young people.
- Access to Sexual and Reproductive Health Services:
- Ensuring access to quality sexual and reproductive health services for all.
- Ensuring access to quality sexual and reproductive health services for all.
- Challenging Stigma and Discrimination:
- Combating stigma and discrimination related to sexuality.
- Combating stigma and discrimination related to sexuality.
- Promoting Gender Equality:
- Advocating for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
- Advocating for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
- Creating Supportive Environments:
- Creating safe and supportive environments for people to discuss and explore their sexuality.
Sexual health is an integral part of overall well-being. By promoting sexual rights, providing access to essential services, and fostering open communication, we can create a society where everyone can enjoy healthy and fulfilling sexual lives.
I hope this information is helpful.
Other Posts